OTHER AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
Pustular psoriasis
Pustular Psoriasis is a kind of psoriasis that develops fast in the form of white pustules.

Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease that classically affects skin and joints and is associated with numerous comorbidities. There are several clinical subtypes of psoriasis including the uncommon pustular variant.
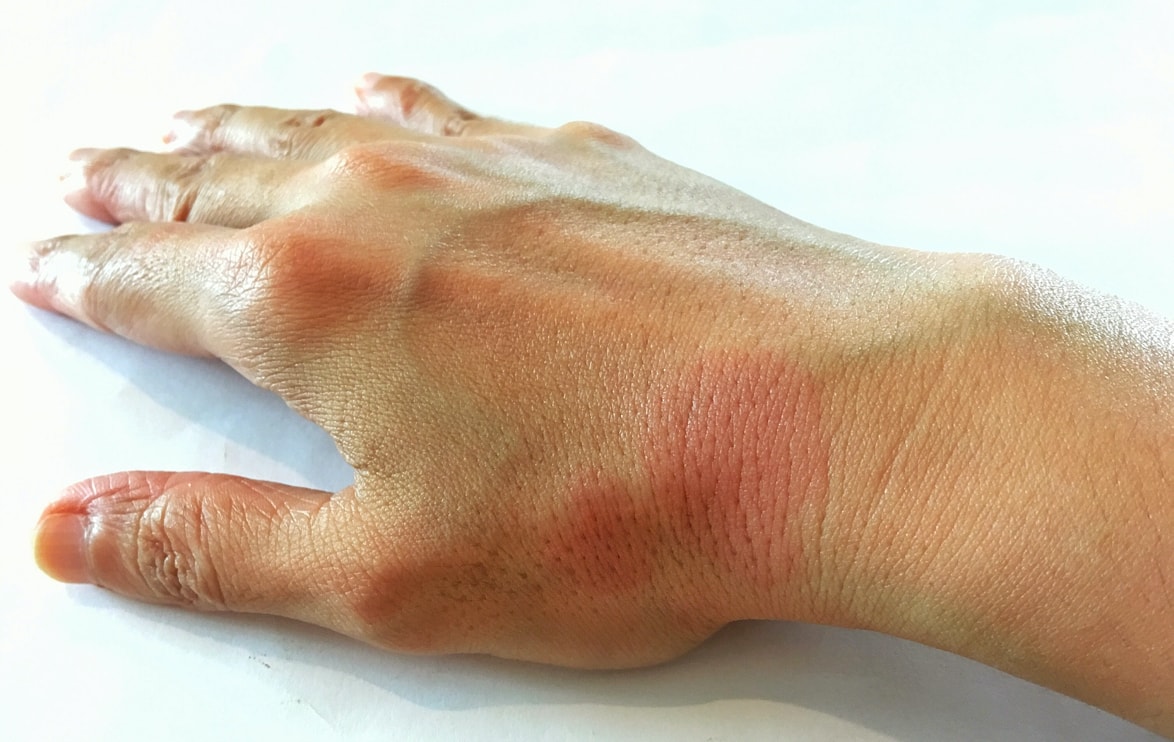
Pustular Psoriasis (PP) accelerates the life cycle of skin cells and causes cells to accumulate rapidly on the skin surface. Is characterized by white pustules (blisters of non-infectious pus of mononuclear and neutrophilic inflammatory infiltrate in the epidermis), surrounded by red skin, oedema and hyperplasia that causes itching and sometimes pain. It usually manifests rapidly, with the onset of pus-filled blisters a few hours after the skin becomes red and sensitive. Generalized PP can also cause fever, chills, severe itching and diarrhoea.
PP is a rare disease marked by recurrent episodes or flares. It affects both children and adults (appears between ages 40 to 50). It can be diffuse or localized in smaller areas on hands, feet or fingertips. Asians tend to be more affected than Caucasians and women and men are affected equally.
A full body skin examination should be performed, including careful evaluation of the mucous membranes and the nails for other signs of psoriasis.
There is no cure for PP, but the symptoms can be controlled. Lifestyle-related measures, such as applying moisturizer, quitting smoking and managing stress, can be helpful.
The main goal of treatment is to stop the accelerated growth of skin cells, prevent infection and fluid loss, stabilize the body’s temperature and restore the skin’s chemical balance. Treatment will vary from person to person depending on their symptoms. A person may need to try more than one treatment or a combination of therapies before finding a suitable one.
Other
Autoimmune
Diseases
Related links
More linksContact UsFor more information
Contact Us